本文目录
- 本题很不错,建议自己思考提交通过后看答案,受益匪浅
题目描述
给你一个长度为 n 的链表,每个节点包含一个额外增加的随机指针 random ,该指针可以指向链表中的任何节点或空节点。
构造这个链表的 深拷贝。 深拷贝应该正好由 n 个 全新 节点组成,其中每个新节点的值都设为其对应的原节点的值。新节点的 next 指针和 random 指针也都应指向复制链表中的新节点,并使原链表和复制链表中的这些指针能够表示相同的链表状态。复制链表中的指针都不应指向原链表中的节点 。
例如,如果原链表中有 X 和 Y 两个节点,其中 X.random --> Y 。那么在复制链表中对应的两个节点 x 和 y ,同样有 x.random --> y 。
返回复制链表的头节点。
用一个由 n 个节点组成的链表来表示输入/输出中的链表。每个节点用一个 [val, random_index] 表示:
val:一个表示 Node.val 的整数。
random_index:随机指针指向的节点索引(范围从 0 到 n-1);如果不指向任何节点,则为 null 。
你的代码 只 接受原链表的头节点 head 作为传入参数。
示例 1:
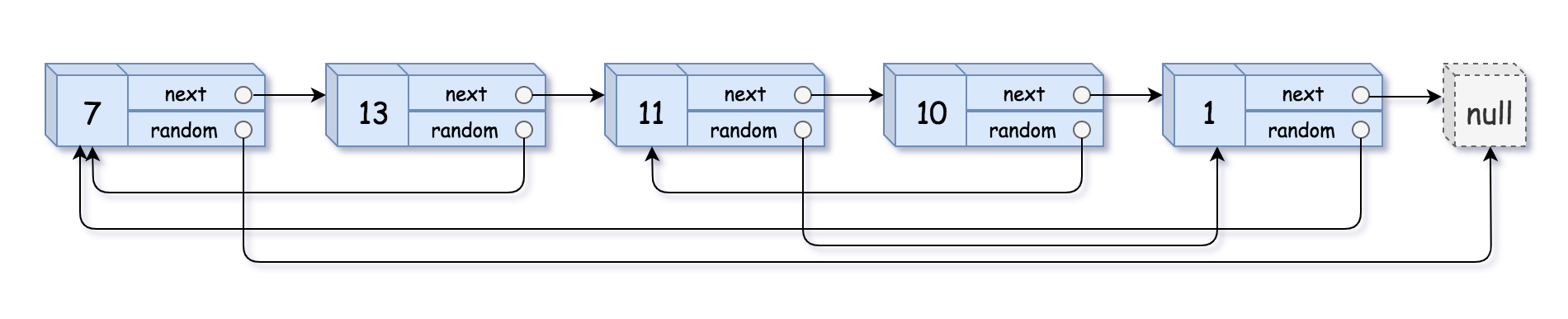
输入:head = [[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]] 输出:[[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]]
示例 2:
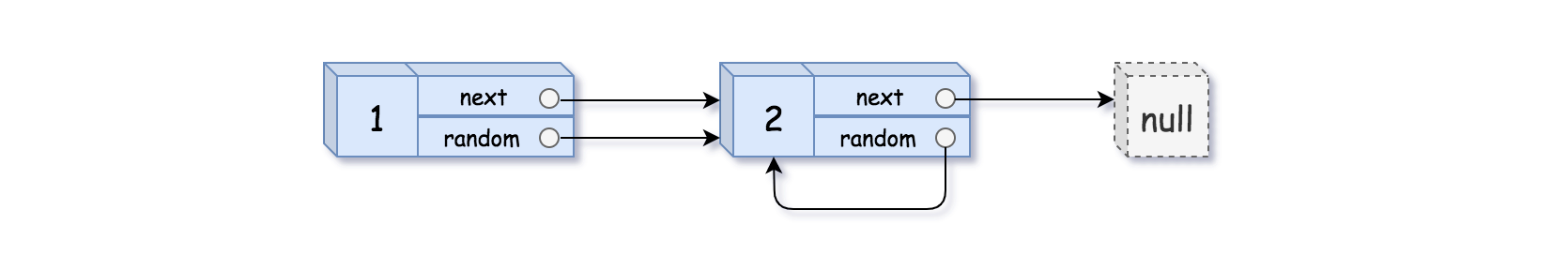
输入:head = [[1,1],[2,1]] 输出:[[1,1],[2,1]]
个人C++解答
GYL
个人思路比较简单,主要就是模拟链表构建,先构建next后构建random,使用哈希表作为辅助random位置查找
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public:
int val;
Node* next;
Node* random;
Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
next = NULL;
random = NULL;
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public:
Node* copyRandomList(Node* head) {
Node* result = new Node(0);
Node *p = result, *q = head;
while (q != nullptr) {
p->next = new Node(q->val);
p = p->next;
q = q->next;
}
// Node* ptr = result->next;
unordered_map<int, int> Map;
q = head;
int key = 1, value = 0;
while (q != nullptr) {
if (q->random != nullptr) {
p = head;
while (p != nullptr) {
value++;
if (p == q->random) {
Map[key] = value;
key++;
value = 0;
break;
}
p = p->next;
}
} else {
Map[key] = 0;
key++;
value = 0;
}
q = q->next;
}
q = result->next;
int count = 1;
while (q != nullptr) {
p = result->next;
int index = 0;
if (Map[count] == 0) {
q->random = nullptr;
index++;
}
while (p != nullptr) {
index++;
if (index == Map[count]) {
q->random = p;
break;
}
p = p->next;
}
count++;
q=q->next;
}
return result->next;
}
};
优质解答
代码解释
第一步:创建所有新的节点并放入哈希表
我们遍历原始链表,并为每个节点创建一个新的节点,同时将原始节点和新节点的映射关系存储在哈希表 nodeMap 中。
第二步:设置新的链表的 next 和 random 指针
我们再次遍历原始链表,通过哈希表将新的节点的 next 和 random 指针设置为对应的节点。
优点
空间复杂度降低:尽管我们仍然使用了哈希表,但避免了额外的多次遍历,从而减少了内存的使用。
时间复杂度:总体时间复杂度为 O(n),因为每个节点只遍历两次。
class Solution {
public:
Node* copyRandomList(Node* head) {
if (!head) return nullptr;
unordered_map<Node*, Node*> nodeMap;
// Step 1: Create all new nodes and put them into the hashmap
Node* current = head;
while (current) {
nodeMap[current] = new Node(current->val);
current = current->next;
}
// Step 2: Set next and random pointers
current = head;
while (current) {
nodeMap[current]->next = nodeMap[current->next];
nodeMap[current]->random = nodeMap[current->random];
current = current->next;
}
return nodeMap[head];
}
};

