本文目录
【本文仅用作笔记和回顾】
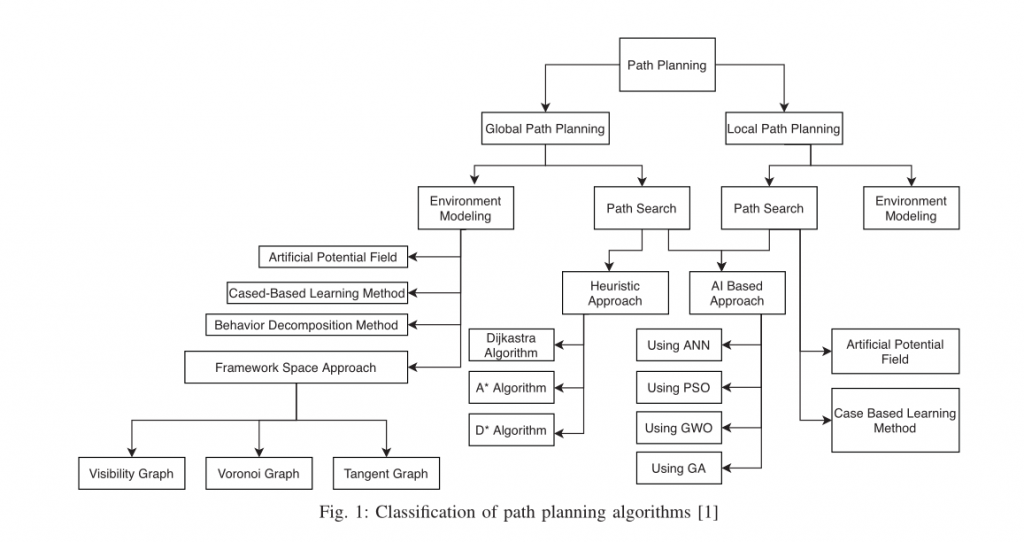
一、前言
以无人驾驶车领域为例介绍全局路径规划和局部路径规划:
(一)全局路径规划:全局路径规划算法属于静态规划算法,根据已有的地图信息(SLAM)为基础进行路径规划,寻找一条从起点到目标点的最优路径。通常全局路径规划的实现包括Dijikstra算法,A * 算法,RRT算法等经典算法,也包括蚁群算法、遗传算法等智能算法;
(二)局部路径规划:局部路径规划属于动态规划算法,是无人驾驶汽车根据自身传感器感知周围环境,规划处一条车辆安全行驶所需的路线,常应用于超车,避障等情景。通常局部路径规划的实现包括动态窗口算法(DWA),人工势场算法,贝塞尔曲线算法等,也有学者提出神经网络等智能算法。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_55205668/article/details/123922046
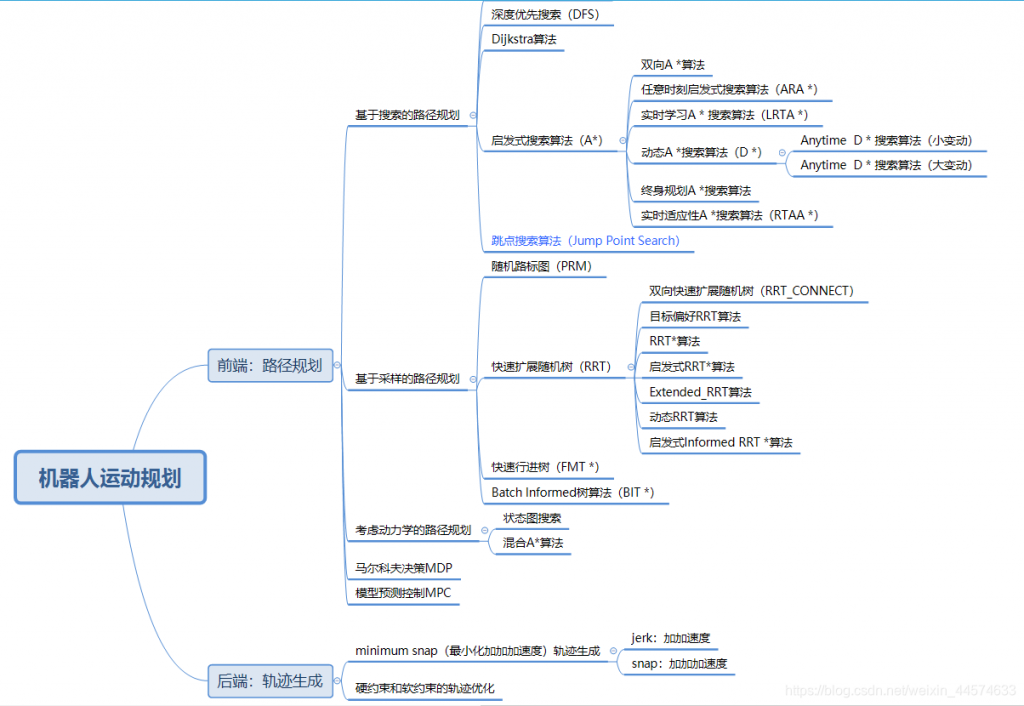
上图来源于:路径规划算法
二、全局路径规划
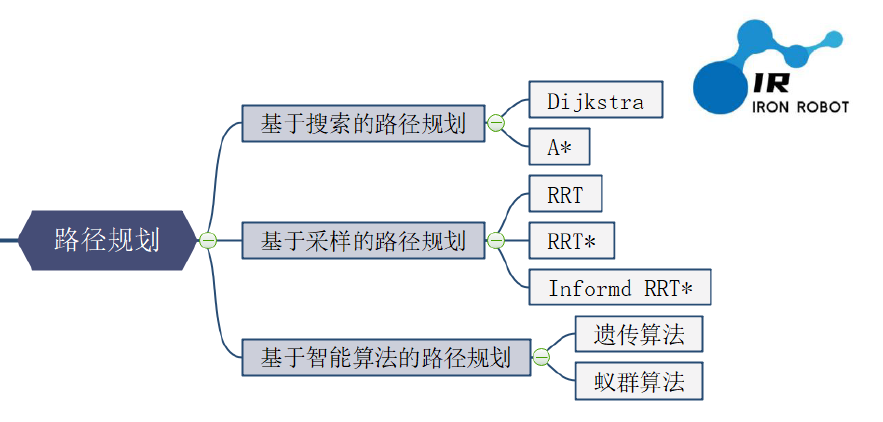
在全局路径规划算法中,大致可分为三类:基于搜索的算法(Dijkstra算法、A* 算法等)、基于采样的算法(RRT、RRT * 等)、智能算法(蚁群、遗传等)。【该分类根据B站IR艾若机器人,下图同】
常用的搜索算法还有D* ,D*Lite,LPA*等,对于 Dijkstra、A* ,D* ,D* Lite,LPA* 这五种算法的比较可以参考 https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/124232080
由于规划岗常见的是Dijkstra 、A* 、D* 、RRT 、RRT* ,本篇将着重写这几个算法,可能还会提及蚁群。
【搜索算法 1 】Dijkstra
可以直接看:
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_44431690/article/details/108175827 ,这篇的过程给的非常详细。
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/346558578 ,这篇的例子给的很清晰,同时给了C#的实现。
https://oi-wiki.org/graph/shortest-path/ ,这篇给出了时间复杂度和正确性证明,同时给出了优先队列实现。
https://www.luogu.com.cn/article/s581e0wm ,洛谷出品,很明显是在算法上进行优化(堆)。
由于数据结构的老师教我它读迪杰斯特拉算法,所以我就保持了这个习惯。Dijkstra可以说是最经典的最短路径算法,利用贪心作为思路,维护两张表:distance(起点到其他所有点的距离信息)、Top_node(最短路径信息)。
其整体逻辑可以理解为进行 n 次循环,每次循环再遍历 n 个点确定一个还未确定最短距离的点中距离源点最近距离的点,然后再用这个点更新其所能到达的点(算法默认当前的点可以到达所有的点,因为没有到达的点之间的距离都已经初始化为正无穷大,所以不会被更新,不影响结果) (https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41575507/article/details/114548187)
实现伪代码:图源 IR艾若机器人
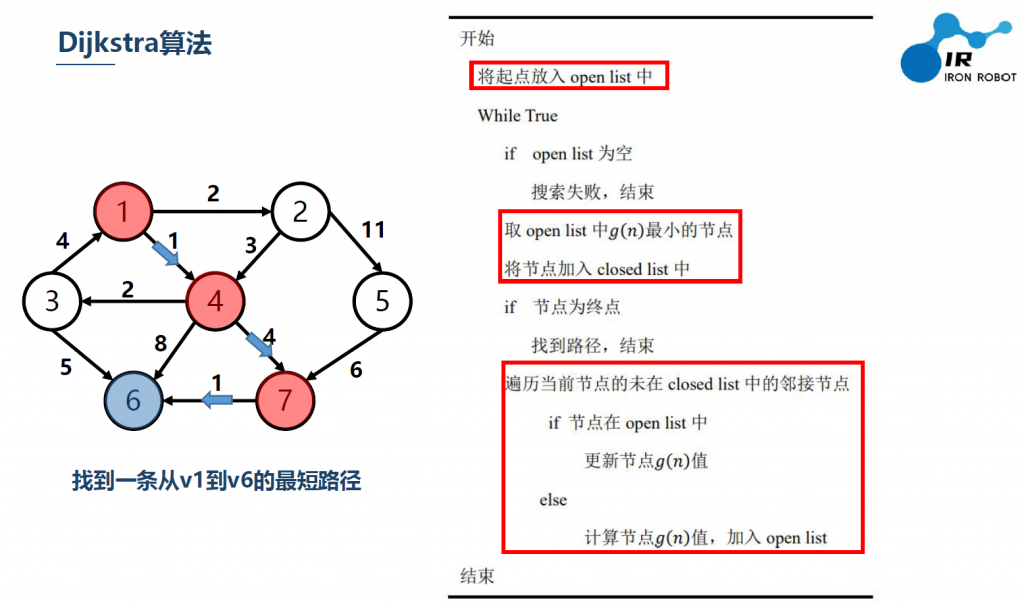
Dijkstra求最短距离伪代码
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_33375598/article/details/104338104
//图G一般设为全局变量;数组d为源点到达各点的最短路径长度,s为起点
Dijkstra(G, d[], s){
初始化
for (循环n次)
{
u = 使d[u]最小的但还未被访问的顶点的标号;
记u已被访问;
for (从u出发能到达的所有顶点v)
{
if(v未被访问 && 以u为中介点使s到顶点v的最短路径d[v]更优){
优化d[v];
}
}
}
}C++ Dijkstra邻接矩阵求最短距离实现
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_33375598/article/details/104338104
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int MAXV = 1000; // 最大顶点数
const int INF = 0x3fffffff; // 定义无穷大
int G[MAXV][MAXV]; // 图的邻接矩阵表示
int d[MAXV]; // 起点到达各点的最短路径
bool vis[MAXV] = { false }; // 标记是否被访问
int n; // 顶点数
void Dijkstra(int s) { // s 是起点
fill(d, d + n, INF); // 将整个数组 d 赋值为 INF
d[s] = 0; // 起点到自身的距离为 0
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { // 循环 n 次
int u = -1, min = INF;
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) { // 找到未访问的顶点中 d[] 最小的
if (!vis[j] && d[j] < min) {
u = j;
min = d[j];
}
}
if (u == -1) return; // 找不到小于 INF 的 d[u],说明剩余顶点不可达
vis[u] = true; // 标记 u 已被访问
for (int v = 0; v < n; ++v) { // 更新 d[v]
if (!vis[v] && G[u][v] != INF && d[u] + G[u][v] < d[v]) {
d[v] = d[u] + G[u][v];
}
}
}
}
int main() {
// 顶点数和边数
n = 5; // 节点个数
int edges[7][3] = { // 定义图的边 (起点, 终点, 权重)
{0, 1, 10},
{0, 4, 5},
{1, 2, 1},
{1, 4, 2},
{2, 3, 4},
{3, 0, 7},
{4, 2, 9}
};
// 初始化图的邻接矩阵
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
fill(G[i], G[i] + n, INF);
// 设置边的权重
for (auto& edge : edges) {
int u = edge[0], v = edge[1], w = edge[2];
G[u][v] = w;
}
// 执行 Dijkstra 算法,以 0 为起点
Dijkstra(0);
// 输出从起点到每个顶点的最短距离
cout << "Shortest distances from vertex 0:" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if (d[i] == INF) cout << "INF ";
else cout << d[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
C++ Dijkstra邻接表求最短距离实现
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_33375598/article/details/104338104
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
struct Node {
int v; // 边的目标顶点
int dis; // 边的权重
};
const int MAXV = 1000; // 最大顶点数
const int INF = 0x3fffffff; // 无穷大表示不可达
vector<Node> Adj[MAXV]; // 邻接表表示的图
int d[MAXV]; // 起点到各个顶点的最短路径
bool vis[MAXV] = { false }; // 标记是否访问过的顶点
int n; // 顶点数
void Dijkstra(int s) { // s 是起点
fill(d, d + n, INF); // 初始化所有最短路径为不可达
d[s] = 0; // 起点到自身的距离为 0
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { // 循环 n 次
int u = -1, min = INF;
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) { // 找到未访问的顶点中 d[] 最小的
if (!vis[j] && d[j] < min) {
u = j;
min = d[j];
}
}
if (u == -1) return; // 找不到小于 INF 的 d[u],说明剩余顶点不可达
vis[u] = true; // 标记 u 已访问
for (int j = 0; j < Adj[u].size(); ++j) { // 更新 d[v]
int v = Adj[u][j].v;
int weight = Adj[u][j].dis;
if (!vis[v] && d[u] + weight < d[v]) {
d[v] = d[u] + weight;
}
}
}
}
int main() {
// 顶点数和边数
n = 5; // 顶点数
int edges[7][3] = { // 图的边定义 (起点, 终点, 权重)
{0, 1, 10},
{0, 4, 5},
{1, 2, 1},
{1, 4, 2},
{2, 3, 4},
{3, 0, 7},
{4, 2, 9}
};
// 初始化邻接表
for (auto& edge : edges) {
int u = edge[0], v = edge[1], w = edge[2];
Adj[u].push_back({ v, w });
}
// 执行 Dijkstra 算法,以 0 为起点
Dijkstra(0);
// 输出从起点到每个顶点的最短路径
cout << "Shortest distances from vertex 0:" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if (d[i] == INF) cout << "INF ";
else cout << d[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
Dijkstra求最短路径伪代码
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_33375598/article/details/104338104
//图G一般设为全局变量;数组d为源点到达各点的最短路径长度,s为起点
Dijkstra(G, d[], s){
初始化
for (循环n次)
{
u = 使d[u]最小的但还未被访问的顶点的标号;
记u已被访问;
for (从u出发能到达的所有顶点v)
{
if(v未被访问 && 以u为中介点使s到顶点v的最短路径d[v]更优){
优化d[v];
令v的前驱为u;
}
}
}
}
C++ Dijkstra邻接矩阵求最短路径实现
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_33375598/article/details/104338104
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int MAXV = 1000;
const int INF = 0x3ffffff;
int G[MAXV][MAXV]; // 图的邻接矩阵
int pre[MAXV]; // 前驱节点数组
int d[MAXV]; // 最短路径数组
bool vis[MAXV] = { false }; // 标记是否被访问
int n; // 顶点数
void Dijkstra(int s) { // 求出最短路径上每个结点的前驱
fill(d, d + n, INF); // 初始化最短路径数组
d[s] = 0; // 起点到自身的距离为 0
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) pre[i] = i; // 初始化前驱数组
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
int u = -1, min = INF;
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if (!vis[j] && d[j] < min) {
u = j;
min = d[j];
}
}
if (u == -1) return; // 找不到小于 INF 的 d[u],说明剩余顶点不可达
vis[u] = true; // 标记 u 已被访问
for (int v = 0; v < n; ++v) { // 更新 d[v] 和 pre[v]
if (!vis[v] && G[u][v] != INF && d[u] + G[u][v] < d[v]) {
d[v] = d[u] + G[u][v];
pre[v] = u;
}
}
}
}
void DFS(int s, int v) { // 递归打印从起点 s 到当前顶点 v 的路径
if (v == s) {
cout << s << " ";
return;
}
DFS(s, pre[v]);
cout << v << " ";
}
int main() {
// 定义图的边数和顶点数
n = 5; // 顶点数
int edges[7][3] = { // 图的边定义 (起点, 终点, 权重)
{0, 1, 10},
{0, 4, 5},
{1, 2, 1},
{1, 4, 2},
{2, 3, 4},
{3, 0, 7},
{4, 2, 9}
};
// 初始化图的邻接矩阵
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
fill(G[i], G[i] + n, INF);
for (auto& edge : edges) {
int u = edge[0], v = edge[1], w = edge[2];
G[u][v] = w;
}
// 以 0 为起点执行 Dijkstra 算法
Dijkstra(0);
// 输出从起点到每个顶点的最短路径
cout << "Shortest distances from vertex 0:" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if (d[i] == INF) cout << "INF ";
else cout << d[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
// 输出从起点到每个顶点的路径
cout << "Paths from vertex 0:" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
cout << "Path to " << i << ": ";
if (d[i] == INF) cout << "No path" << endl;
else {
DFS(0, i); // 打印从 0 到 i 的路径
cout << endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
C++ Dijkstra邻接表求最短路径实现
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_33375598/article/details/104338104
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
struct Node {
int v; // 目标顶点
int dis; // 边的权重
};
const int MAXV = 1000;
const int INF = 0x3ffffff;
vector<Node> Adj[MAXV]; // 邻接表表示的图
int pre[MAXV]; // 前驱节点数组
int d[MAXV]; // 最短路径数组
bool vis[MAXV] = { false }; // 标记是否被访问
int n; // 顶点数
void Dijkstra(int s) { // 求出最短路径上每个结点的前驱
fill(d, d + n, INF); // 初始化最短路径数组
d[s] = 0; // 起点到自身的距离为 0
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) pre[i] = i; // 初始化前驱数组
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
int u = -1, min = INF;
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) { // 找到未访问的顶点中 d[] 最小的
if (!vis[j] && d[j] < min) {
u = j;
min = d[j];
}
}
if (u == -1) return; // 找不到小于 INF 的 d[u],说明剩余顶点不可达
vis[u] = true; // 标记 u 已被访问
for (int j = 0; j < Adj[u].size(); ++j) { // 更新 d[v] 和 pre[v]
int v = Adj[u][j].v;
int weight = Adj[u][j].dis;
if (!vis[v] && d[u] + weight < d[v]) {
d[v] = d[u] + weight;
pre[v] = u;
}
}
}
}
void DFS(int s, int v) { // 递归打印从起点 s 到当前顶点 v 的路径
if (v == s) {
cout << s << " ";
return;
}
DFS(s, pre[v]);
cout << v << " ";
}
int main() {
// 顶点数和边数
n = 5; // 顶点数
int edges[7][3] = { // 定义图的边 (起点, 终点, 权重)
{0, 1, 10},
{0, 4, 5},
{1, 2, 1},
{1, 4, 2},
{2, 3, 4},
{3, 0, 7},
{4, 2, 9}
};
// 初始化邻接表
for (auto& edge : edges) {
int u = edge[0], v = edge[1], w = edge[2];
Adj[u].push_back({ v, w });
}
// 执行 Dijkstra 算法,以 0 为起点
Dijkstra(0);
// 输出从起点到每个顶点的最短路径
cout << "Shortest distances from vertex 0:" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if (d[i] == INF) cout << "INF ";
else cout << d[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
// 输出从起点到每个顶点的路径
cout << "Paths from vertex 0:" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
cout << "Path to " << i << ": ";
if (d[i] == INF) cout << "No path" << endl;
else {
DFS(0, i); // 打印从 0 到 i 的路径
cout << endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
Dijkstra 优先队列 优化
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/34624812
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
struct Edge {
int to; // 目标顶点
int cost; // 边的权重
};
const int MAXV = 1000; // 最大顶点数
const int INF = 0x3ffffff; // 无穷大表示不可达
vector<Edge> G[MAXV]; // 邻接表表示的图
int d[MAXV]; // 最短路径数组
int n; // 顶点数
void Dijkstra(int s) { // 求出从起点 s 到其他顶点的最短路径
fill(d, d + n, INF); // 初始化距离
d[s] = 0; // 起点到自身的距离为 0
priority_queue<pair<int, int>, vector<pair<int, int>>, greater<pair<int, int>>> que; // 小顶堆
que.push({ 0, s }); // 将起点推入队列
while (!que.empty()) {
auto p = que.top(); // 获取队头元素
que.pop();
int v = p.second; // 当前顶点编号
if (d[v] < p.first) continue; // 跳过已处理的顶点
for (const auto& e : G[v]) { // 遍历邻接边
if (d[e.to] > d[v] + e.cost) { // 松弛操作
d[e.to] = d[v] + e.cost; // 更新距离
que.push({ d[e.to], e.to }); // 将更新后的顶点推入队列
}
}
}
}
int main() {
// 定义图的边和顶点数
n = 5; // 顶点数
int edges[7][3] = { // 定义图的边 (起点, 终点, 权重)
{0, 1, 10},
{0, 4, 5},
{1, 2, 1},
{1, 4, 2},
{2, 3, 4},
{3, 0, 7},
{4, 2, 9}
};
// 初始化邻接表
for (auto& edge : edges) {
int u = edge[0], v = edge[1], w = edge[2];
G[u].push_back({ v, w });
}
// 执行 Dijkstra 算法,以 0 为起点
Dijkstra(0);
// 输出从起点到每个顶点的最短路径
cout << "Shortest distances from vertex 0:" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if (d[i] == INF) cout << "INF ";
else cout << d[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
【搜索算法 2】 A *
首先,https://paul.pub/a-star-algorithm/ 这篇文章写得很好,我基本都是抄这篇的;
其次,https://tashaxing.blog.csdn.net/article/details/47152137 这篇是我一开始学A* 的时候看的,也算是入门文章,当时在vs下编写运行的;后来在学 A* 的改进的时候对其进行了修改;
最后,https://github.com/lh9171338/Astar 这篇是我到现在一直在用的,因为我懒得再写一份,它用优先队列进行存储,算是对最基础的A* 进行了改进
很多地方都在说A* 引入启发式函数巴拉巴拉什么的,说白了,就是给搜索路线上的每个位置都评价打分一下,然后排个序选个最优点去走,整体理解起来我个人认为要比Dijkstra要简单的多的。
A * 算法实现伪代码
图源艾若机器人

初始化open_set和close_set;
* 将起点加入open_set中,并设置优先级为0(优先级最高);
* 如果open_set不为空,则从open_set中选取优先级最高的节点n:
* 如果节点n为终点,则:
* 从终点开始逐步追踪parent节点,一直达到起点;
* 返回找到的结果路径,算法结束;
* 如果节点n不是终点,则:
* 将节点n从open_set中删除,并加入close_set中;
* 遍历节点n所有的邻近节点:
* 如果邻近节点m在close_set中,则:
* 跳过,选取下一个邻近节点
* 如果邻近节点m也不在open_set中,则:
* 设置节点m的parent为节点n
* 计算节点m的优先级
* 将节点m加入open_set中
启发函数:
f(n) = g(n) + h(n)
g(n)表示单次移动耗费,h(n)表示到目标点的预计耗费,f(n)则为综合代价。
g(n)很好理解,就是我从这一格走到下一格需要耗费的代价,在栅格地图中当前位置存在8个邻居节点,移动也只会移动到8个邻居节点上,所以此时的代价就只有两种情况 1 或者 sqrt(2) ,也就对应着直走或者斜走。
h(n)在我看来更好理解,就是节点到目标点耗费的代价,代价的方式有很多种,使用规则如下:
- 如果图形中只允许朝上下左右四个方向移动,则可以使用曼哈顿距离(Manhattan distance)。
- 如果图形中允许朝八个方向移动,则可以使用对角距离。
- 如果图形中允许朝任何方向移动,则可以使用欧几里得距离(Euclidean distance)。
①曼哈顿距离
计算曼哈顿距离的函数如下,这里的D是指两个相邻节点之间的移动代价,通常是一个固定的常数。
function heuristic(node) =
dx = abs(node.x - goal.x)
dy = abs(node.y - goal.y)
return D * (dx + dy)②对角距离
计算对角距离的函数如下,这里的D2指的是两个斜着相邻节点之间的移动代价。如果所有节点都正方形,则其值就是sqrt(2) * D
function heuristic(node) =
dx = abs(node.x - goal.x)
dy = abs(node.y - goal.y)
return D * (dx + dy) + (D2 - 2 * D) * min(dx, dy)③欧几里得距离
如果图形中允许朝任意方向移动,则可以使用欧几里得距离。
欧几里得距离是指两个节点之间的直线距离,因此其计算方法也是我们比较熟悉的,其函数表示如下:
function heuristic(node) =
dx = abs(node.x - goal.x)
dy = abs(node.y - goal.y)
return D * sqrt(dx * dx + dy * dy)C++实现
这里贴的代码是本人优化后的,初始的代码是参考 https://tashaxing.blog.csdn.net/article/details/47152137 这篇文章的
Astar.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "AStar.h"
namespace pathplanning {
void Astar::InitAstar(vector<vector<int>>& _Map) {
Map = _Map;
Map_rows = _Map.size();
Map_cols = _Map[0].size();
}
int Astar::CalcG(Point* _curpoint, Point* _point) {
int extraG = (abs(_point->x - _curpoint->x) + abs(_point->y - _curpoint->y)) == 1 ? 10 : 14;
int parentG = _point->parent == nullptr ? 0 : _point->parent->G;
return parentG + extraG;
}
int Astar::CalcH(Point* _targetpoint, Point* _endpoint) {
int dist = (_endpoint->x - _targetpoint->x) * (_endpoint->x - _targetpoint->x) + (_endpoint->y - _targetpoint->y) * (_endpoint->y - _targetpoint->y);
return round(10 * sqrt(dist));
}
int Astar::CalcF(Point* _point) {
return _point->G + _point->H;
}
void Astar::PathPlanning(Point _startPoint, Point _targetPoint, vector<pair<int, int>>& path) {
startPoint = _startPoint;
endPoint = _targetPoint;
Point* TailPoint = FindPath(isIgnoreCorner);
GetPath(TailPoint, path);
}
Point* Astar::isInCloseList(const vector<Point*>& _closelist, const Point* point) const
{
for (auto p : _closelist)
if (p->x == point->x && p->y == point->y)
return p;
return nullptr;
}
Point* Astar::isInOpenList(const priority_queue<pair<int, Point*>, vector<pair<int, Point*>>, cmp>& _openlist, const Point* point) const
{
priority_queue<pair<int, Point*>, vector<pair<int, Point*>>, cmp> temp = _openlist;
while (!temp.empty()) {
Point* p = temp.top().second;
temp.pop();
if (p->x == point->x && p->y == point->y) {
return p;
}
}
return nullptr;
}
bool Astar::isCanreach(const Point* _point, const Point* _targetPoint) const
{
if (_targetPoint->x<0 || _targetPoint->x>Map.size() - 1
|| _targetPoint->y<0 || _targetPoint->y>Map[0].size() - 1
|| Map[_targetPoint->x][_targetPoint->y] == 1
|| _targetPoint->x == _point->x && _targetPoint->y == _point->y
|| isInCloseList(CloseList, _targetPoint))
return false;
else
{
if (abs(_point->x - _targetPoint->x) + abs(_point->y - _targetPoint->y) == 1) //非斜角可以
return true;
else
{
if (Map[_point->x][_targetPoint->y] == 0 && Map[_targetPoint->x][_point->y] == 0)
return true;
else
return isIgnoreCorner;
}
}
}
vector<Point*> Astar::getSurroundPoints(const Point* _point) const {
vector<Point*>SurroundPoints;
#if Neibor5 == 1
/* 5邻域*/
int dx = endPoint.x - _point->x;
int dy = endPoint.y - _point->y;
if (dx >= 0 && dy >= 0) {
addSurroundPoint(SurroundPoints, _point->x - 1, _point->y - 1, _point);
addSurroundPoint(SurroundPoints, _point->x - 1, _point->y , _point);
addSurroundPoint(SurroundPoints, _point->x - 1, _point->y + 1, _point);
addSurroundPoint(SurroundPoints, _point->x , _point->y + 1, _point);
addSurroundPoint(SurroundPoints, _point->x + 1, _point->y + 1, _point);
}
else if (dx >= 0 && dy <= 0) {
addSurroundPoint(SurroundPoints, _point->x - 1, _point->y + 1, _point);
addSurroundPoint(SurroundPoints, _point->x , _point->y + 1, _point);
addSurroundPoint(SurroundPoints, _point->x + 1, _point->y - 1, _point);
addSurroundPoint(SurroundPoints, _point->x + 1, _point->y , _point);
addSurroundPoint(SurroundPoints, _point->x + 1, _point->y + 1, _point);
}
else if (dx <= 0 && dy >= 0) {
addSurroundPoint(SurroundPoints, _point->x - 1, _point->y - 1, _point);
addSurroundPoint(SurroundPoints, _point->x - 1, _point->y , _point);
addSurroundPoint(SurroundPoints, _point->x - 1, _point->y + 1, _point);
addSurroundPoint(SurroundPoints, _point->x , _point->y - 1, _point);
addSurroundPoint(SurroundPoints, _point->x + 1, _point->y - 1, _point);
}
else if (dx <= 0 && dy <= 0) {
addSurroundPoint(SurroundPoints, _point->x - 1, _point->y - 1, _point);
addSurroundPoint(SurroundPoints, _point->x , _point->y - 1, _point);
addSurroundPoint(SurroundPoints, _point->x + 1, _point->y - 1, _point);
addSurroundPoint(SurroundPoints, _point->x + 1, _point->y , _point);
addSurroundPoint(SurroundPoints, _point->x + 1, _point->y + 1, _point);
}
#else
for (int x = _point->x - 1; x <= _point->x + 1; x++)
for (int y = _point->y - 1; y <= _point->y + 1; y++)
if (isCanreach(_point, new Point(x, y)))
SurroundPoints.push_back(new Point(x, y));
#endif
return SurroundPoints;
}
// 辅助函数,用于添加可达的邻域点
void Astar::addSurroundPoint(vector<Point*>& SurroundPoints, int x, int y, const Point* _point) const {
if (isCanreach(_point, new Point(x, y))) {
SurroundPoints.push_back(new Point(x, y));
}
}
Point* Astar::FindPath(bool isIgnoreCorner) {
// Add startPoint to OpenList
Point* startPointNode = new Point(startPoint.x, startPoint.y);
OpenList.push(pair<int, Point*>(startPointNode->F, startPointNode));
int index = point2index(*startPointNode);
OpenDict[index] = startPointNode;
while (!OpenList.empty()) {
// Find the node with least F value
Point* CurPoint = OpenList.top().second;
OpenList.pop();
int index = point2index(*CurPoint);
Point* CurNode = OpenDict[index];
OpenDict.erase(index);
// Determine whether arrive the target point
if (CurPoint->x == endPoint.x && CurPoint->y == endPoint.y)
{
return CurNode; // Find a valid path
}
CloseList.push_back(CurPoint);
// Find the accessible node around the Current node
auto SurroundPoints = getSurroundPoints(CurPoint);
for (auto& targetPoint : SurroundPoints) {
if (!OpenDict.count(point2index(*targetPoint))) {
//if (!isInOpenList(OpenList, targetPoint)) {
targetPoint->parent = CurPoint;
targetPoint->G = CalcG(CurPoint, targetPoint);
targetPoint->H = CalcH(targetPoint, &endPoint);
targetPoint->F = CalcF(targetPoint);
OpenList.push(pair<int, Point*>(targetPoint->F, targetPoint));
int index = point2index(*targetPoint);
OpenDict[index] = targetPoint;
}
else {
int TempG = CalcG(CurPoint, targetPoint);
if (TempG < targetPoint->G) {
targetPoint->parent = CurPoint;
targetPoint->G = TempG;
targetPoint->F = CalcF(targetPoint);
}
}
/*
Point* resPoint = isInOpenList(OpenList, &endPoint);
if (resPoint)
return resPoint; //返回列表里的节点指针,不要用原来传入的endpoint指针,因为发生了深拷贝
*/
}
}
return nullptr;
}
void Astar::GetPath(Point* TailNode, vector<pair<int, int>>& path) {
PathList.clear();
path.clear();
// Save path to PathList
Point* CurNode = TailNode;
while (CurNode != nullptr)
{
PathList.push_back(CurNode);
CurNode = CurNode->parent;
}
// Save path to vector<Point>
int length = PathList.size();
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++)
{
path.push_back(pair<int, int>(PathList.back()->x, PathList.back()->y));
PathList.pop_back();
}
// Release memory
while (OpenList.size()) {
OpenList.pop();
}
CloseList.clear();
}
}
Astar.h
//
// Created by GuoYulong on 24-8-23.
//
#ifndef ASTAR_H
#define ASTAR_H
#define Neibor5 0
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <unordered_map>
using namespace std;
constexpr auto isIgnoreCorner = true;;
namespace pathplanning {
struct Point {
int x, y;
int F, G, H;
Point* parent;
Point(int _x, int _y) :x(_x), y(_y), F(0), G(0), H(0), parent(nullptr) {
}
};
struct cmp
{
bool operator() (pair<int, Point*> a, pair<int, Point*> b) // Comparison function for priority queue
{
return a.first > b.first; // min heap
}
};
class Astar {
public:
Astar() :startPoint(0, 0), endPoint(0, 0), Map(), Map_cols(0), Map_rows(0), OpenList(), CloseList(), PathList() {
}
void InitAstar(vector<vector<int>>& _Map);
void PathPlanning(Point _startPoint, Point _targetPoint, vector<pair<int, int>>& path);
inline int point2index(Point point) {
return point.y * Map_cols + point.x;
}
inline Point index2point(int index) {
return Point(int(index / Map_cols), index % Map_cols);
}
private:
Point* FindPath(bool isIgnoreCorner);
void GetPath(Point* TailNode, vector<pair<int, int>>& path);
bool isCanreach(const Point* _point, const Point* _targetPoint) const;
void addSurroundPoint(vector<Point*>& SurroundPoints, int x, int y, const Point* _point) const;
vector<Point*> getSurroundPoints(const Point* _point) const;
Point* isInCloseList(const vector<Point*>& _closelist, const Point* point) const;
Point* isInOpenList(const priority_queue<pair<int, Point*>, vector<pair<int, Point*>>, cmp>& _openlist, const Point* point) const;
int CalcG(Point* _startpoint, Point* _point);
int CalcH(Point* _point, Point* _targetpoint);
int CalcF(Point* _point);
private:
Point startPoint, endPoint;
vector<vector<int>> Map;
int Map_cols, Map_rows;
priority_queue<pair<int, Point*>, vector<pair<int, Point*>>, cmp> OpenList;
unordered_map<int, Point*> OpenDict;
vector<Point*> CloseList;
vector<Point*> PathList;
};
}
#endifA * 的优化
①程序上优化复杂度
A * 算法的核心计算在于:
1.从open和close表中进行查找
2.从open表中搜索最小栅格
3.从邻居中查找最小栅格
考虑从①②两点进行优化,传统的 A * 使用 vector<Point * > 或者 list<Point* >(Point为自己定义的点的结构体,包括坐标,FGH,父节点)
考虑到查找的复杂度较高,所以思考采用hash表进行查找,其查找的复杂度为O(1),所以我们采用unordered_map 对 openlist 和 closelist 进行备份,在查找时直接调用查找函数find或者count,由于unordered_map存在键值对应关系,可以设计为点的坐标的序号为key,即 (point.x-1)*map.col+point.y ,这样能确保唯一性;
考虑到排序的复杂度较高,快排也有O(nlog)的复杂度,所以使用priority_queue结构来存储openlist,即先前给出的代码中的 priority_queue<pair<int, Point*>, vector<pair<int, Point*>>, cmp> OpenList 。
注意:事实上,在我的代码中并没有对closelist进行哈希表备份,主要是懒得改了,如果读者有需要的话可以在Astar.h中进行修改,这样就不需要函数InCloseList了。
②优化启发函数 F(N) = G(N)+W(N)*H(N)
参考文章: A* 算法及优化思路
在应用中就是动态加权,在H(N)较大时W(N)也应较大,当H(N)较小时W(N)也应较小,但这样修改的话,搜索出的路径并不是最优路径,但时间可以大大缩短;W(N)可以根据H(N)自行设定。
③优化邻域
参考:依据象限搜索及混合预计耗费的A*改进算法,包含8邻域及24邻域的改进
根据目标点与当前点的位置关系将邻域缩小一角,由于我的代码是基于8邻域的没测试24邻域,在8邻域下修改为5邻域时间缩短1/3左右(在测试的时候我将地图扩大到1000点左右为了效果更加明显)
④使用双向A*算法
并不是一个比较稳定的做法,后续如果使用到后再做补充
参考:双向A*搜索 | 双向启发式搜索(有几个关键问题做出了解答)
⑤其他优化方法
参考文章:【路径规划】A*算法方法改进思路简析
【搜索算法 3】 D *
D* 是Dynamic A* 的简写,其算法和A* 类似,不同的是,其代价的计算在算法运行过程中可能会发生变化。
D * 包含了下面三种增量搜索算法:
1.原始的D* 由Anthony Stentz发表。
2.Focussed D* 由Anthony Stentz发表,是一个增量启发式搜索算法,结合了A* 和原始D* 的思想。
3.D*Lite是由Sven Koenig和Maxim Likhachev基于LPA* 构建的算法。
所有三种搜索算法都解决了相同的基于假设的路径规划问题,包括使用自由空间假设进行规划。在这些环境中,机器人必须导航到未知地形中的给定目标坐标。它假设地形的未知部分(例如:它不包含障碍物),并在这些假设下找到从当前坐标到目标坐标的最短路径。
然后机器人沿着路径行进。当它观察到新的地图信息(例如以前未知的障碍物)时,它会将信息添加到其地图中,并在必要时将新的最短路径从其当前坐标重新添加到给定的目标坐标。它会重复该过程,直到达到目标坐标或确定无法达到目标坐标。在穿越未知地形时,可能经常发现新的障碍,因此重新计划需要很快。增量(启发式)搜索算法通过使用先前问题的经验来加速搜索当前问题,从而加速搜索类似搜索问题的序列。假设目标坐标没有改变,则所有三种搜索算法都比重复的A* 搜索更有效。
D* 及其变体已广泛用于移动机器人和自动车辆导航。当前系统通常基于D*Lite而不是原始D* 或Focussed D* 。
D * 算法实现伪代码
下述内容(伪代码部分),摘自https://blog.csdn.net/rezrezre/article/details/131008284 推荐去看,写的很不错
function Dstar(map, start, end):
# map:m*n的地图,记录了障碍物。map[i][j]是一个state类对象
# start:起点,state类对象
# end: 终点,state类对象
open_list = [ ] # 新建一个open list用于引导搜索
insert_to_openlist(end,0, open_list) # 将终点放入open_list中
# 第一次搜索,基于离线先验地图找到从起点到终点的最短路径,注意从终点往起点找
loop until (start.t == “close”):
process_state() # D*算法核心函数之一
end loop
# 让机器人一步一步沿着路径走,有可能在走的过程中会发现新障碍物
temp_p = start
while (p != end) do
if ( unknown obstacle found) then # 发现新障碍物, 执行重规划
for new_obstacle in new_obstacles: # 对每个新障碍物调用modify_cost函数
modify_cost( new_obstacle ) #(D*算法核心函数之一)
end for
do
k_min = process_state()
while not ( k_min >= temp_p.h or open_list.isempty() )
continue
end if
temp_p = temp_p.parent
end while 上述伪代码中核心函数为2个:modify_cost 和 process_state
下面是modify_cost的伪代码:
function modify_cost( new_obstacle ):
set_cost(any point to new_obstacle ) = 10000000000 # 让“从任何点到障碍点的代价”和“从障碍点到任何点的代价” 均设置为无穷大,程序中使用超级大的数代替(考虑8邻接)
if new_obstacle.t == "close" then
insert(new_obstacle, new_obstacle.h ) # 放到open表中,insert也是d*算法中的重要函数之一
end if下面是 Process_state函数的伪代码:
function process_state( ):
x = get_min_k_state(oepn_list) # 拿出openlist中获取k值最小那个state,这点目的跟A*是一样的,都是利用k值引导搜索顺序,但注意这个k值相当于A*算法中的f值(f=g+h, g为实际代价函数值,h为估计代价启发函数值),而且在D*中,不使用h这个启发函数值, 仅使用实际代价值引导搜索,所以其实硬要说,D*更像dijkstra,都是使用实际代价引导搜索而不用启发函数缩减搜索范围,D*这点对于后面发现新障碍物进行重新规划来说是必要的。
if x == Null then return -1
k_old = get_min_k(oepn_list) # 找到openlist中最小的k值,其实就是上面那个x的k值
open_list.delete(x) # 将x从open list中移除, 放入close表
x.t = "close" # 相当于放入close表,只不过这里不显式地维护一个close表
# 以下为核心代码:
# 第一组判断
if k_old < x.h then # 满足这个条件说明x的h值被修改过,认为x处于raise状态
for each_neighbor Y of X: #考虑8邻接neighbor
if y.h<k_old and x.h> y.h + cost(y,x) then
x.parent = y
x.h = y.h + cost(x,y)
end if
end for
end if
# 第二组判断
if k_old == x.h then
for each_neighbor Y of X: #考虑8邻接neighbor
if y.t== "new" or
(y.parent == x and y.h !=x.h + cost(x,y) ) or
(y.parent != x and y.h >x.h + cost(x,y)) then
y.parent = x
insert(y, x.h + cost(x,y))
end if
end for
else: # 不满足k_old == x.h 那就是k_old < x.h
for each_neighbor Y of X: #考虑8邻接neighbor
if y.t == "new" or
(y.parent == x and y.h !=x.h + cost(x,y) ) then
y.parent = x
insert(y, x.h + cost(x,y))
else:
if (y.parent != x and y.h >x.h + cost(x,y)) then
x.k = x.h # 注意这行!没有这行会出现特定情况死循环。在查阅大量资料后,在wikipedia的d*算法页面中找到解决办法就是这行代码。网上大部分资料,包括d*原始论文里都是没这句的,不知道为啥
insert(x, x.h)
else:
if (y.parent!=x and x.h>y.h+cost(y,x) and y.t= "close" and y.h>k_old then
insert(y,y.h)
end if
end if
end if
end for
end if
return get_min_k(oepn_list) C++ 实现
< 待补充 >
由于D* 强调的是在障碍地图改变后防止重新全局规划而对A*的调整,“障碍物改变”这一情况在仿真中不太好搞,所以先不做这部分的处理。
【搜索算法 4】 LPA *
< 待补充 >
【采样算法 1】 RRT 与 RRT*
< 待补充 >
相对于上述提到的所有算法,RRT更好理解,整体步骤就是【 采样->找最近点连线->判断是否通过障碍物->取点 】循环进行这个步骤,直到达到目标点范围内,然后连接最短的路径。可以根据原理就可以看出,RRT并不能得出最优路径,只是能找到一条路径,但是谁让它快啊,很多时候最优并不是必须,快速反应才比较好。
不过RRT也有局限,在狭窄道路生成的较慢,毕竟路线中只要有障碍物就不采用这个点的策略确实会导致这个问题。
【采样算法 2】 PRM
< 待补充 >
局部路径规划
< 待补充 >
人工势场法
< 待补充 >
DWA
< 待补充 >
TEB
< 待补充 >